With the relentless advancement of technology, the utilization of mobile phones and internet services has become ubiquitous across the globe. As a result, an increasing number of people are embracing VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) services to conduct their phone calls.
VoIP represents a revolutionary technology that enables the transmission of voice over internet networks. In this groundbreaking process, your spoken words undergo a seamless transformation into digital data, gracefully traversing the internet to reach their intended destination.
Yet, the key to seamless voice transmission through VoIP lies in the proficient use of codecs. Codecs, akin to sophisticated software alchemists, adeptly compress audio data packets, paving the way for their swift journey through internet networks.
Given the vast array of VoIP codecs available in today’s tech landscape, achieving pristine call sound quality necessitates a keen understanding of the fundamental principles. In this enlightening blog, we shall embark on an exploration of the diverse VoIP codecs, delving into their profound impact on call sound quality.
What Are VoIP Codecs?
VoIP codecs are essential software tools responsible for compressing audio data packets, enabling their transmission over internet networks, and subsequently decompressing them at the destination for audio playback.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology utilizes the internet to facilitate phone calls, converting sound into digital data. The audio data is then compressed using specific codecs suitable for VoIP, enabling efficient transmission over the internet. At the receiving end, the compressed data is decompressed using a compatible codec to restore it into audible sound.
Various VoIP codecs each come with their own strengths and weaknesses. One widely used codec is G.711, favored for its high-quality phone calls. However, it utilizes more bandwidth due to lower compression.
On the other hand, codecs like G.729 offer higher compression, leading to reduced bandwidth usage, but they compromise call sound quality.
Some advanced VoIP codecs like Opus feature noise reduction and additional settings, tailored to enhance voice quality in challenging network conditions.
Optimizing sound quality involves carefully adjusting codec parameters. While higher compression ratios may provide better performance, excessive codec tweaking can lead to decreased sound quality and introduce noise.
Moreover, network quality directly impacts the VoIP call experience. Weak internet connections can result in data packet loss or improper reception, leading to delays and disruptions in communication. Correctly configuring codec and network settings can mitigate such issues, ensuring smoother interactions with your audience.
Principles of Sound Quality in VoIP Communication
In today’s business landscape, a reliable VoIP system has become indispensable for countless companies. Effective business communication hinges on loyalty, making the quality of voice calls a crucial factor.
To better understand audio processing, it’s essential to familiarize ourselves with key terms related to audio quality:
Sample Rate (Sampling Frequency): This refers to the number of audio samples received per second. A higher sampling rate results in better sound quality, as it captures more details and nuances of the voice.
Bitrate: Bitrate signifies the amount of data converted into audio. Higher audio bitrate means more audio data is recorded per second. Generally, a higher bitrate translates to improved sound quality, providing clearer and more accurate representations of the voice.
Bandwidth: Bandwidth measures the speed of data transmission, encompassing both receiving and sending data. In the context of VoIP, it refers to the number of audio samples transferred per second. Sufficient bandwidth is essential for delivering smooth, uninterrupted communication.
In practice, even if a person’s voice is exceptional, low bitrates can severely impact the quality of communication. A low bitrate will result in the other party struggling to hear clearly, leading to a subpar communication experience. Therefore, ensuring an optimal sample rate, bitrate, and bandwidth are crucial for maintaining excellent sound quality in VoIP communication.
How HD Voice Improves Call Quality
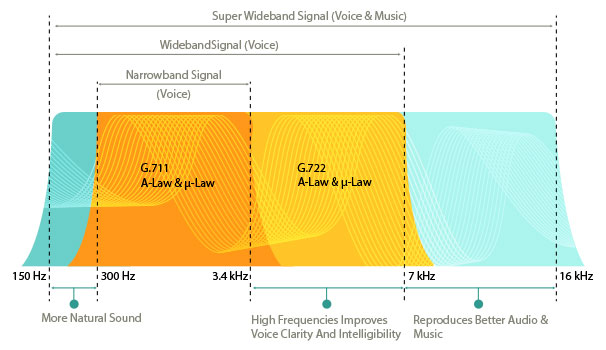
HD Voice, a cutting-edge technology in VoIP, significantly enhances the sound quality of phone calls by transmitting a broader range of frequencies within the telephone frequency spectrum. This advanced approach reduces errors and imperfections in call sound, resulting in a substantial improvement in call quality.
HD Voice primarily focuses on two audio bands: narrowband and wideband. In the narrowband, frequencies above 3400 Hz experience a significant increase, allowing for better clarity and detail in the transmitted sound. In the wideband, the use of a broader band combines more frequencies, further enhancing sound quality.
The integration of HD Voice into phone calls brings about a remarkable difference in audio quality, transforming the calling experience into something truly unique and satisfying.
Additionally, in VoIP communication, audio codecs play a vital role in encoding and compressing voice data. Let’s explore three popular types of codecs:
G.711: One of the oldest and widely used VoIP codecs, G.711 was designed for analog voice compression and VoIP network utilization. It employs the Linear Predictive Coding algorithm, resulting in high sound quality. However, due to its higher data transmission, it is not ideal for networks with limited bandwidth.
G.722 HD: This codec aims to deliver high-quality conversational voice in VoIP through superior compression techniques. Widely used in mobile applications and office systems, G.722 HD enables transmission of sound in higher quality, making it sound more lifelike and natural.
G.729: Developed specifically for networks with restricted bandwidth, G.729 is among the most widely used VoIP codecs. It achieves substantial data reduction, ensuring acceptable sound quality. However, due to higher data compression, its sound quality is slightly lower compared to the other two codecs.
Each of these codecs caters to different network conditions and priorities, enabling users to choose the one that best suits their specific requirements for sound quality and bandwidth efficiency.
VoIP Codecs Categories
VoIP codecs can be categorized based on their compression capabilities, dividing them into two main groups: codecs with weak compression and codecs with strong compression. Codecs with strong compression are ideal for networks with limited bandwidth, as they significantly reduce the amount of data sent. However, this enhanced compression may slightly lower the sound quality compared to codecs with weaker compression.
Below are examples of VoIP codecs organized according to their compression capabilities:
Codecs with weak compression:
- G.711
- G.722
- iLBC
- G.726
- G.728
Codecs with strong compression:
- G.723.1
- G.729
- GSM
- Speex
- Opus
Each codec serves specific VoIP needs. For instance, G.711 is well-suited for person-to-person conversations in organizations due to its high voice quality. On the other hand, G.729 is more appropriate for business-to-business conversations over networks with limited bandwidth.
In conclusion, VoIP codecs play a crucial role in determining call sound quality. By selecting appropriate codecs, it is possible to enhance call sound quality and provide a superior user experience. The discussed codecs – G.711, G.729, and G.722 HD – each have their own advantages and disadvantages. However, the right choice of codecs can enable beneficial features such as noise reduction and improved sound quality.







